e-Campsis
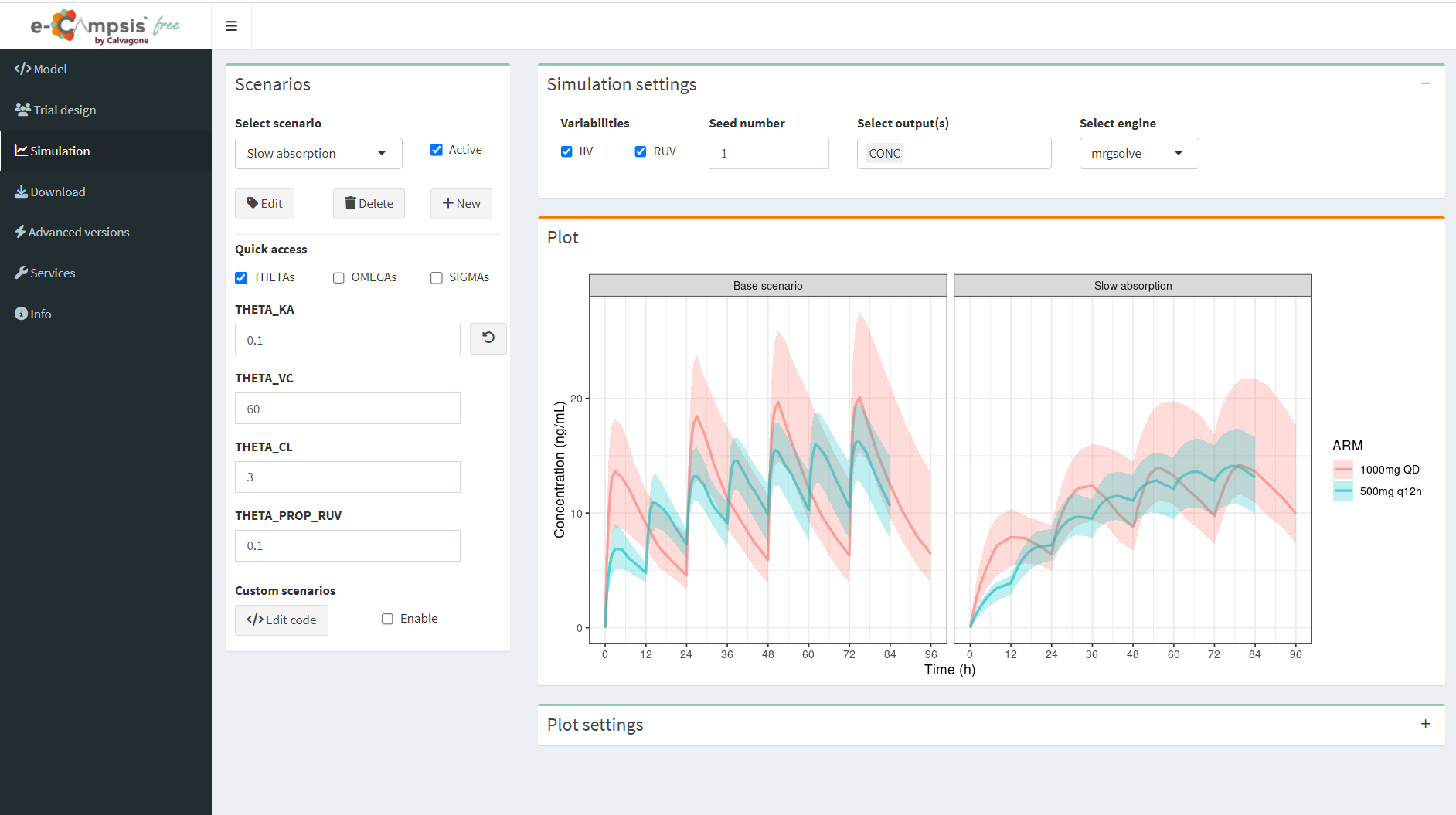
e-Campsis® is a free web application developed by Calvagone that provides an intuitive and user-friendly interface for setting up population PK/PD simulations. The app is built on the R-package campsis, which serves as a powerful frontend for running model-based simulations using mrgsolve or rxode2.
Go to e-campsis.com for more information and try the free version today!